- Teacher: Mrs. Meena .
Available courses
- Teacher: Dr. (Mrs.) Seema .
- Teacher: Dr. Rachna Dalal
- Teacher: Dr. Rachna Dalal
Micro Economics is that branch of economics that studies the behaviour of individuals
and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the
interactions among these individuals and firms. In micro economics, the following
theories are dealt with:
Demand theory deals with consumers’ behaviour. It answers such questions
as: How do the consumers decide whether or not to buy a commodity? How do
they decide on the quantity of a commodity to be purchased? When do they stop
consuming a commodity? How do the consumers behave when price of the
commodity, their income and tastes and fashions, etc., change? At what level of
demand, does changing price become inconsequential in terms of total revenue?
The knowledge of demand theory can, therefore, be helpful in making the choice
of commodities, finding the optimum level of production and in determining the
price of the product.
Production theory explains the relationship between inputs and output. It
also explains under what conditions costs increase or decrease; how total output
behaves when units of one factor (input) are increased keeping other factors
constant, or when all factors are simultaneously increased; how can output be
maximized from a given quantity of resources; and how can the optimum size of
output be determined? Production theory, thus, helps in determining the size of the
firm, size of the total output and the amount of capital and labour to be employed,
given the objective of the firm.
Price theory explains how price is determined under different kinds of market
conditions; when price discrimination is desirable, feasible and profitable; and to
what extent advertising can be helpful in expanding sales in a competitive market.
Thus, price theory can be helpful in determining the price policy of the firm.
Price and production theories together, in fact, help in determining the optimum
size of the firm. Profit making is the most common objective of all business
undertakings. But, making a satisfactory profit is not always guaranteed because a
firm has to carry out its activities under conditions of uncertainty with regard to: (i)
demand for the product, (ii) input prices in the factor market, (iii) nature and
degree of competition in the product market, and (iv) price behaviour under
changing conditions in the product market, etc. Therefore, an element of risk is
always there even if the most efficient techniques are used for predicting the future
and even if business activities are meticulously planned. The firms are, therefore,
supposed to safeguard their interest and avert or minimize the possibilities of risk.
Profit theory guides firms in the measurement and management of profit, in
making allowances for the risk premium, in calculating the pure return on capital
and pure profit and also for future profit planning.

- Teacher: Dr. Priyanka Sahni
- Teacher: Miss Natisha .
- Teacher: Miss Natisha .
- Teacher: Miss Natisha .
- Teacher: Mrs. Kokila .
- Teacher: Mrs. Nischal Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Nischal Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Soni .
- Teacher: Mrs. Arti Saini .
- Teacher: Mrs. Arti Saini .
- Teacher: Mrs. Arti Saini .
- Teacher: Dr. Priya Sharma
- Teacher: Dr. Priya Sharma
- Teacher: Dr. Priya Sharma
- Teacher: Dr. Priya Sharma
- Teacher: Dr. Jyoti .
- Teacher: Mrs. Shivani Garg
- Teacher: Dr. Jyoti .
motion
- Teacher: suman gill
- Teacher: suman gill
- Teacher: Miss Anju .
- Teacher: Miss Bindu .
- Teacher: Miss Bindu .
- Teacher: Mrs. Ritu .
- Teacher: Mrs. Ritu .
- Teacher: Menka .
- Teacher: Shreya Bansal
- Teacher: Mrs. Shiromani Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Shiromani Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Shiromani Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Shiromani Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Poonam .
- Teacher: Mrs. Poonam .
- Teacher: Mrs. Poonam .
- Teacher: Mrs. Priya Goel
- Teacher: Mrs. Priya Goel
- Teacher: Mrs. Priya Goel
- Teacher: Miss Meenakshi .
- Teacher: Miss Meenakshi .
Database technology involves designing, implementing, and maintaining systems for storing, retrieving, and managing data efficiently and securely. A database is a structured collection of data, while the software used to manage it is known as a Database Management System (DBMS). The field is foundational to modern computer applications, including websites, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and financial transactions.
- Teacher: Sunita -

- Teacher: Mrs. Shivani Garg
- Teacher: Mrs. Shiromani Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Prachi .
- Teacher: Mrs. Prachi .
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema .
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema .
- Teacher: Mrs. Kokila .
- Teacher: Mrs. Kokila .
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema .
- Teacher: Miss Purnima Bawalia
- Teacher: Miss Purnima Bawalia
- Teacher: Sunita -
- Teacher: Mrs. Ritu .
- Teacher: Mrs. Ritu .
- Teacher: Suman Saini
- Teacher: suman gill

- Teacher: Sunita -
- Teacher: Mamta Sharma
- Teacher: Mamta Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Nishu Garg
- Teacher: Miss Shivani -
- Teacher: Miss Shivani -
- Teacher: Miss Sonia -
- Teacher: Mrs. Shashi Gautam
- Teacher: Miss Rajkesh Beniwal
- Teacher: Meena Malik
- Teacher: Meena Malik
- Teacher: Kavita Deswal
- Database design: Includes relational data modeling, entity-relationship modeling, and database design theory
- Database management: Includes database security, administration, and transaction processing
- Database implementation: Includes data definition and manipulation languages, and query coding practices
- Database technologies: Includes XML, RD, OWL, parallel, and noSQL databases
- Database applications: Includes web-based database applications and multi-tier client/server architectures
- Data normalization: Includes functional dependencies, non-loss decomposition, and first, second, and third normal forms
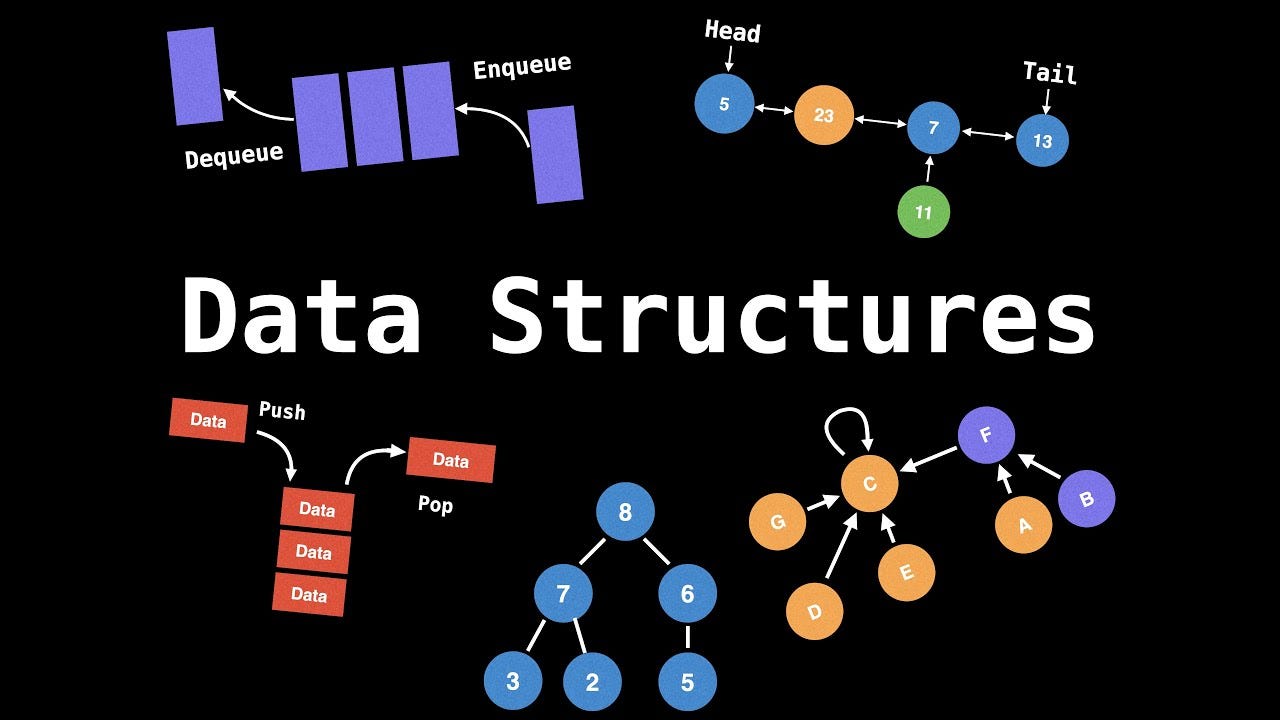
- Data structures and file organizations: Includes concepts and principles of data structures and file organizations
- Data analysis: Includes data and query optimization

- Teacher: Mrs. Nischal Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Ritu .
- Teacher: suman gill
- Teacher: anju -
- Teacher: anju -
- Teacher: anju -
- Teacher: kavita -
- Teacher: kavita -
- Teacher: Mamta Sharma
- Teacher: Mamta Sharma
- Teacher: Nancy Malik
- Teacher: Nancy Malik
- Teacher: Nancy Malik
MATLAB is a high-level programming language and interactive environment widely used in engineering, mathematics, and scientific computing. It allows users to perform computation, visualization, and data analysis in a single environment. MATLAB stands for "MATRIX LABORATORY," emphasizing its powerful capabilities for matrix operations, which are fundamental in many scientific and engineering applications. It provides a vast array of built-in functions for tasks ranging from basic arithmetic to advanced signal processing and machine learning. MATLAB also supports the creation of user-defined functions and scripts, enabling customization and automation of tasks. Its plotting and visualization tools make it easy to generate various types of graphs and charts for data analysis and presentation. Additionally, MATLAB integrates seamlessly with other programming languages and software, making it a versatile tool for scientific research, engineering design, and algorithm development.
- Teacher: Mrs. Shivani Garg
- Teacher: Ms. Geeta .
- Teacher: Ms. Geeta .
- Teacher: Ms. Geeta .
- Teacher: Mrs. Rekha .
- Teacher: Mrs. Rekha .
- Teacher: Mrs. Anjali Singh
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema Sharma
- Teacher: Mrs. Seema Sharma
- Teacher: Dr. Jyoti .
- Teacher: Dr. Jyoti .